Talent Attraction and Fair Recruitment Process
Principles for Talent Attraction and a fair Recruitment Process in Academia
Attracting scientific talent from underrepresented domains can pose distinct challenges. To effectively tackle this issue, institutions must take proactive steps to establish themselves as inclusive and diverse organizations, with a strong emphasis on gender equality, equity, diversity, and inclusion. This entails fostering a research culture and work environment that nurtures inclusivity, offers equal opportunities, and facilitates the success of all individuals. By prioritizing these initiatives and fostering a welcoming atmosphere, institutions can attract and retain exceptionally skilled scientists, thus enhancing the richness and vibrancy of their research community. By removing barriers and biases from the recruitment process, institutes can tap into a wider talent pool and benefit from diverse perspectives, ideas, and approaches. The following principles target especially high-profile scientific candidates from underrepresented domains.
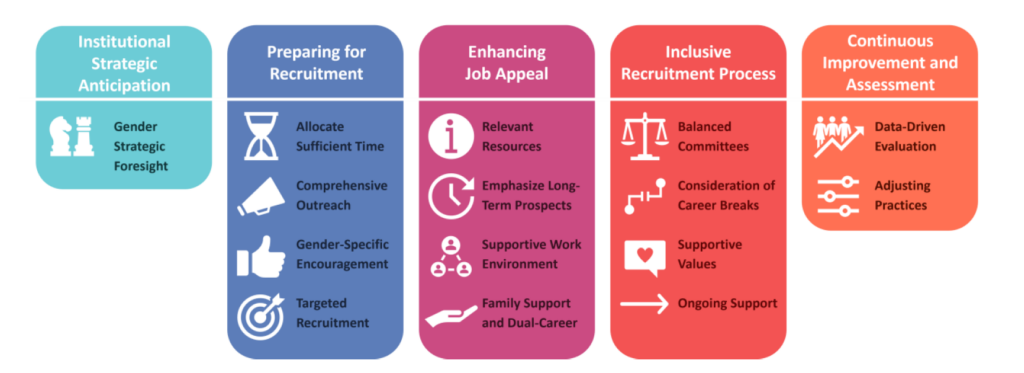
Institutional Strategic Anticipation
- Gender Strategic Foresight: Consider the complete overview of new positions and planned and anticipated retirements. Plan proactively in departments where either gender is currently underrepresented (<40%) and align with the institution’s Gender Equality Plan.
Preparing for Recruitment
- Allocate Sufficient Time: Reserve ample time and in advance of publishing the job description, as this is the foremost step in fostering an inclusive approach to attract talent.
- Comprehensive Outreach: Advertise job openings through diverse channels to attract a wide range of candidates. This includes relevant networks, databanks, events, platforms, engage with professional networks, associations, communities, and professional organizations, focusing on underrepresented groups, gender diversity, and inclusion.
- Gender-Specific Encouragement: Encourage applications from underrepresented genders in areas or roles where clear disparities exist.
- Targeted Recruitment: Implement proactive measures to identify and approach a list of pre-selected candidates from underrepresented genders, employing personalized strategies and direct contact.
Enhancing Job Appeal
- Relevant Resources: Provide comprehensive information about Luxembourg, including the research landscape but also general advantages of the country. Example: the Foreign Researcher’s Guide by Euraxess Luxembourg
- Emphasize Long-Term Prospects: Highlight opportunities for long-term career growth and retention to attract candidates.
- Supportive Work Environment: Provide information on professional development and training opportunities to support career growth, as well as support mechanisms, such as mentoring or networking programs where individuals in similar positions can share experiences and provide guidance on navigating life in Luxembourg.
- Family Support and Dual-Career: Provide information on work-life balance initiatives within the organization and offer support for childcare, housing, as well as offer dual-career options whenever possible.
Inclusive Recruitment Process
- Balanced Committees: Compose recruitment committees with balanced gender representation (40-60% for each gender).
- Consideration of Career Breaks: Account for career breaks in candidate evaluation, applying international best practices. Whenever academic age matters, international recommendations and best practices should be applied (e.g. for ERC grants the eligibility period can be extended for maternity and paternity
- Supportive Values: If candidates from an underrepresented group are unavailable, consider hiring individuals showing a commitment to support gender balance, diversity, and inclusion.
- Ongoing Support: Establish clear onboarding processes to help new employees integrate smoothly into the organization and their respective roles.
Continuous Improvement and Assessment
- Data-Driven Evaluation: Regularly assess the effectiveness of recruitment practices by analyzing demographic data, gender representation, retention rates, and applicant success rates.
- Adjusting Practices: Based on regular assessment outcomes, develop, and implement targeted recruitment strategies, and adjust approaches.
Best Practices for a Fair Recruitment Process
A fair and inclusive recruitment process forms the foundation for providing equal opportunities to all applicants, regardless of their gender, race, ethnicity, sexual orientation, religion, disability, age, or other factors that should not influence their professional choices or career prospects. Such a process is essential for fostering an environment where individuals can pursue research and establish scientific or non-scientific careers based on merit and qualifications alone. It has been shown over the years that unconscious biases with respect to culture, nationality, gender etc. are present frequently during recruitment processes. Facing such a situation can narrow down more and more the profiles in an institute which can lead to a situation where it becomes challenging to change the status and increase the diversity. The reputation of an institute with this respect must not be underestimated.
An inclusive and transparent recruitment process ensures that all candidates have an equal chance to showcase their skills, knowledge, and experience, leading to the selection of the most qualified individuals for positions. By raising awareness to biases and aiming to remove potential barriers and discrimination from the recruitment process, institutes can tap into a wider talent pool and benefit from diverse perspectives, ideas, and approaches.
By consistently implementing best practices for a fair recruitment process, research performing and funding institutions can effectively attract and retain a diverse pool of talented individuals. This, in turn, creates a work environment that prioritizes fairness, equality, and inclusivity, enabling employees to thrive and reach their full potential without experiencing discrimination or conscious bias.
Creating a gender-balanced work environment is a specific goal of a fair recruitment process. Gender equality is crucial for fostering innovation, productivity, and overall organizational success. Research shows that inclusive job application messaging can remove perceived barriers to success that prevent women from entering the technology workforce (source: “More Women in Tech? Evidence from a field experiment addressing social identity”, Lucía Del Carpio, Maria Guadalupe (2019)). Therefore, it is essential to critically evaluate and up-date procedures in place for each step of the recruitment process.
These guidelines apply to all levels of recruitment, from entry-level positions to senior and executive roles and are recommended for individuals responsible for any step of the recruitment process, whether in administrative or scientific positions, within research performing or research funding institutions in Luxembourg. This includes management personnel, HR employees, members of recruitment committees, Gender Equality Officers, and the Staff Delegation Equality Delegate.
The different steps of the recruitment process
A critical aspect of ensuring inclusiveness and fairness is to consistently assess potential sources of unconscious bias. It is essential to continuously evaluate, monitor, and improve existing recruitment procedures for all the steps of the recruitment process. The guidelines outlined below serve as the foundation for enhancing the current state of gender balance in research within Luxembourg, while allowing for further advancements based on experience and time. Herein, best practices are provided for setting up recruitment procedures that aim to avoid commonly perceived issues regarding inequalities in the context of scientific and/or administrative positions.
Furthermore, it is crucial to align these guidelines with each institution’s Gender Equality Plan (GEP), which may or may not include further diversity and inclusion action points and adhere to quantitative gender equality goals. Considering a gender objective serves as an additional initiative to promote gender balance and can be reviewed and adjusted annually by each institution. Equally, consider any specific requirements that may vary depending on the context and your organizational policies.
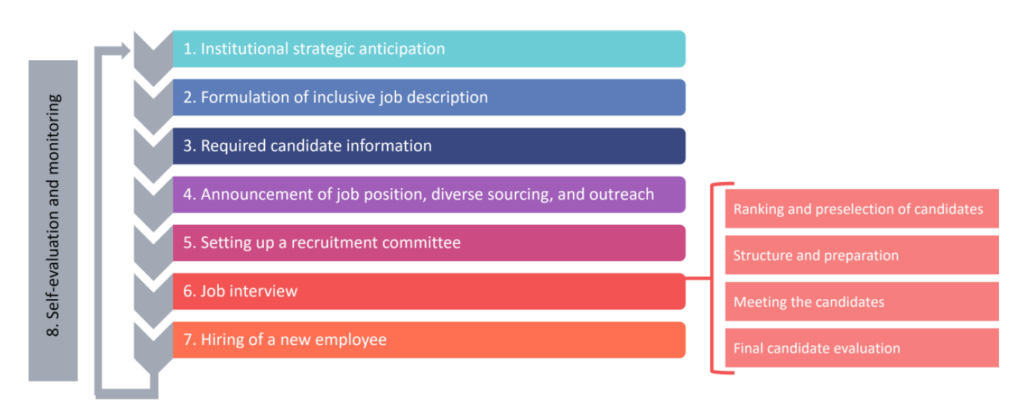
The 7 Steps of the recruitment process:
- Institutional Strategic Anticipation
- Formulation of an inclusive job description
- Required candidate information
- Announcement of the job position, diverse sourcing, and outreach
- Setting up a recruitment committee
- Job interview, including ranking and preselection of candidates, structure and preparation, meeting the candidates, and final candidate evaluation
- Hiring of a new employee
At the end of this process, self-evaluation and monitoring are recommended to ensure continuous improvement and accountability over time.
Download the Best Practices for a fair Recruitment Process document for more details on each step.
Attracting high-profile scientific candidates from an underrepresented gender
Attracting scientific talent from the underrepresented gender to specific research domains can pose distinct challenges. To effectively tackle this issue, institutions must take proactive steps to establish themselves as inclusive and diverse organizations, with a strong emphasis on equity, diversity, and inclusion. This entails fostering a research culture and work environment that nurtures inclusivity, offers equal opportunities, and facilitates the success of individuals from underrepresented backgrounds. By prioritizing these initiatives and fostering a welcoming atmosphere, institutions can attract and retain exceptionally skilled scientists from underrepresented domains, thus enhancing the richness and vibrancy of their research community.
Besides the general best practices elucidated above for a fair recruitment process, the following best practices target especially high-profile scientific candidates from underrepresented backgrounds, such as gender, and can be regrouped into three additional categories, including recommendations on cultural change, recruitment procedures and additional support initiatives.
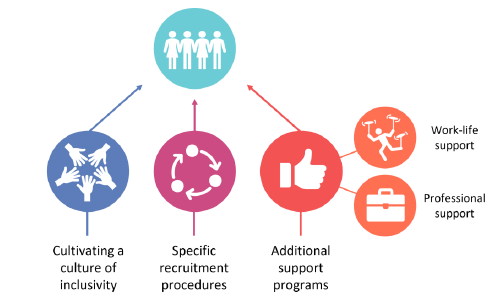
These best practices are:
- Cultivating a culture of inclusivity
- Specific recruitment procedures
- Additional support programs
See more details for each best practices in the document below or download the Best Practices For a Fair Recruitment Process document here